Vietnam Geography
Vietnam has a total land area of over 331,000 km2 and a coastline spreading over 3,200 km.
Location
Vietnam is located at the southeastern tip of the Indochina peninsula. It shares borders with China to the north and Laos and Cambodia to the west. The eastern and southern borders are flanked by the sea, providing Vietnam with abundant aquatic resources, including extensive beaches and rich marine biodiversity. The country has an elongated S-shape, measuring approximately 1,650 km in length, with its narrowest point being about 50 km wide.
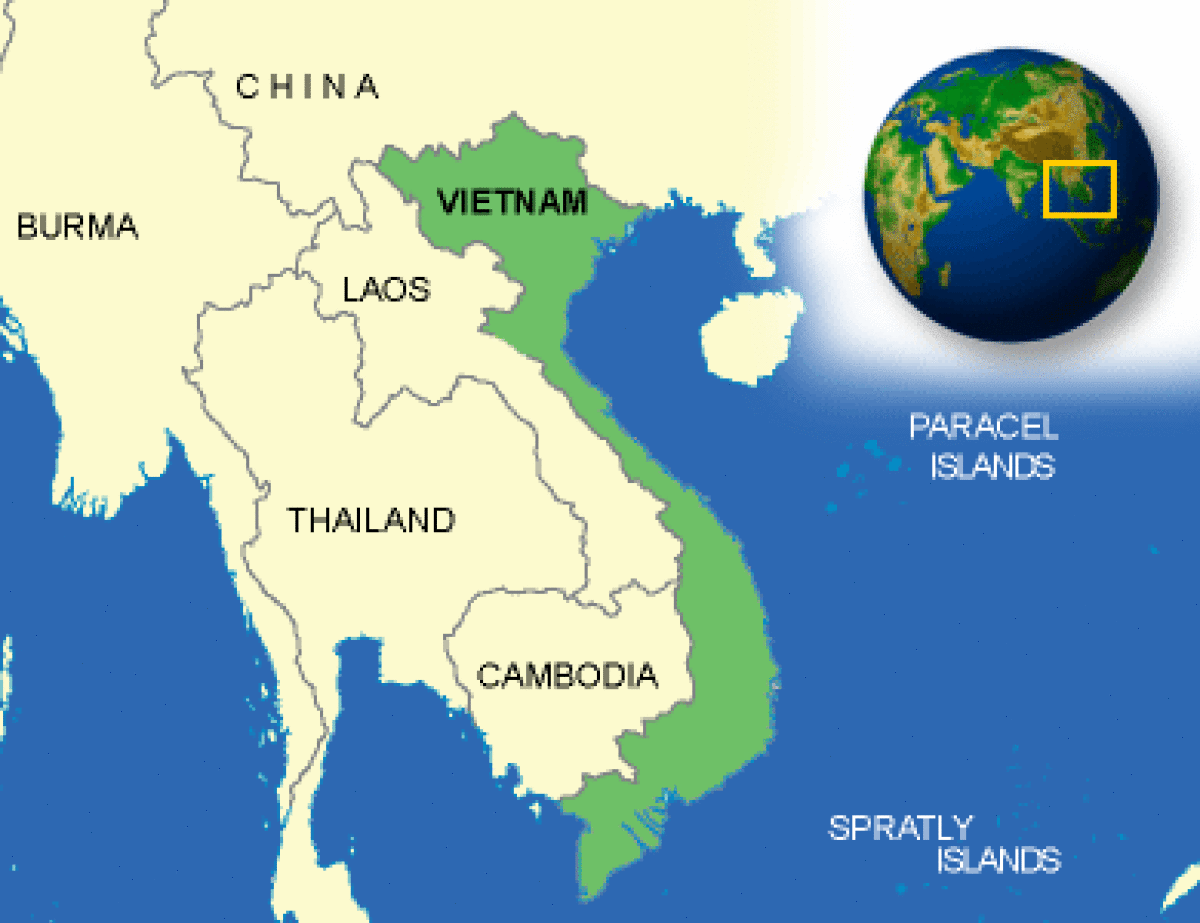 Photo: countryreports.org
Photo: countryreports.org
Area
Land: 331,212 km².
Coastline: 3,260 km.
Terrain
A significant portion of Vietnam's land is characterized by hills and mountains. The cultivable area comprises less than 20% of the total land, primarily situated in the two key river deltas: the Red River delta in the north and the Mekong delta in the south. Although the Red River delta is smaller than its southern counterpart, it is more densely populated and historically significant as the cradle of early Vietnamese civilization.
Main cities and towns include Hanoi, Thai Binh, Nam Dinh, and Ho Chi Minh City. To the south, the Mekong delta boasts the largest agricultural land area and is the primary producer of rice and other staples for both domestic consumption and export. Due to its low-lying geography, there are increasing concerns that the Mekong Delta will be severely impacted by climate change, particularly rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
The mountainous regions encompass the Northern highlands and Central highlands. The challenging weather conditions and unique soil types make rice cultivation difficult in these areas. However, in the northern region, farmers utilize terraced paddy fields to optimize the limited water resources available for rice cultivation. Vietnam is also home to Fansipan, which rises 3,143 meters and is the highest peak in the Indochina peninsula.








